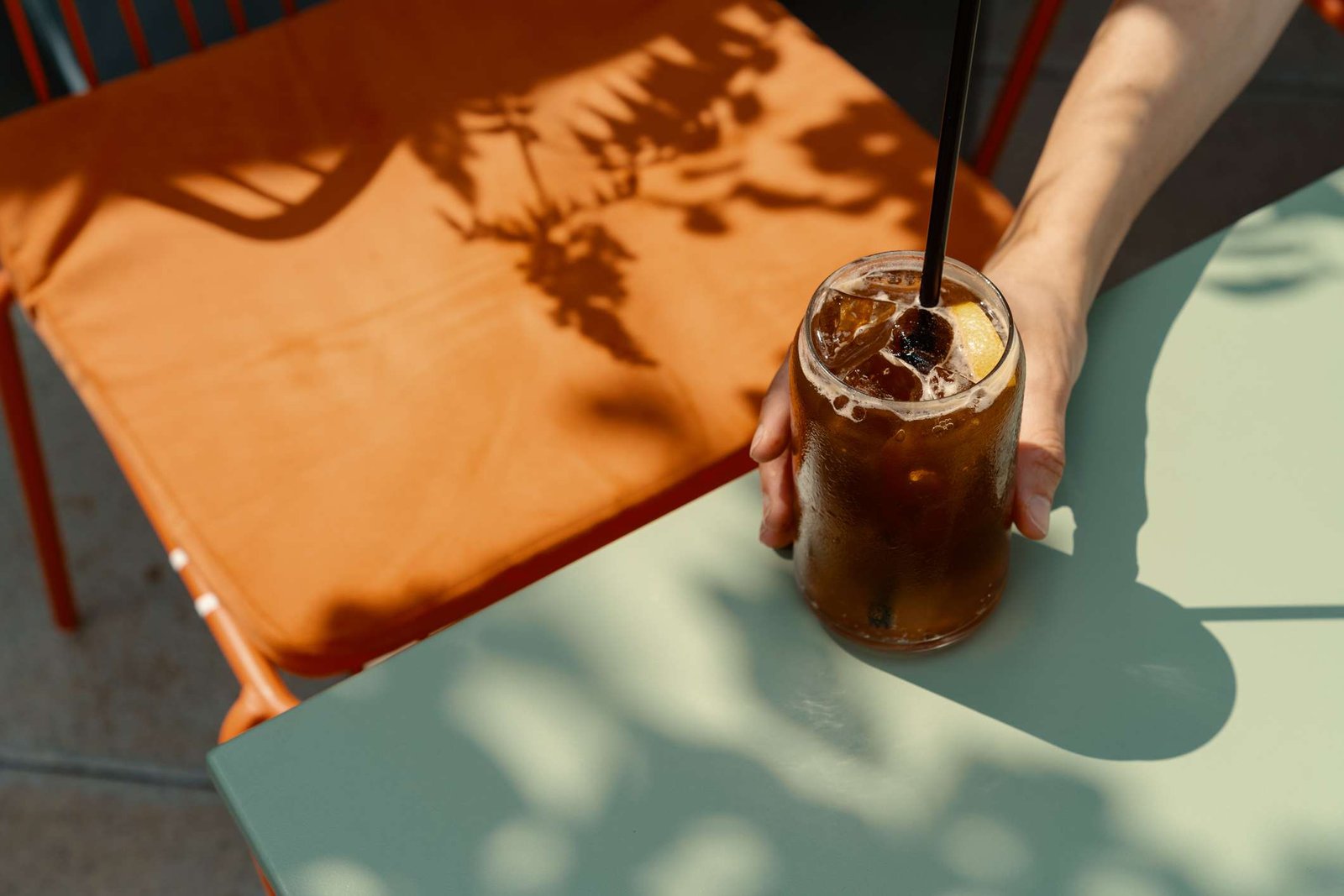
Sipping on caffeinated beverages, like espresso and lattes, can give you a temporary mood and energy boost. But how long does caffeine stay in your system?
Here’s what to know about caffeine’s half-life, plus the amount of caffeine found in your favorite coffee orders.
Caffeine is absorbed pretty quickly into your system, usually within 45 minutes of consuming it. “Peak caffeine levels are seen between 15 minutes and up to two hours, depending on the person’s individual absorption and reaction,” Kelly Jones, MS, RD, CSSD, board-certified sports dietitian, told Health. It kind of depends on whether you consume it with other foods.
In healthy people, the half-life of caffeine is about five hours, meaning it will take you around five hours, on average, to clear out 50% of the caffeine you consumed from your body.
The time it takes your body to metabolize caffeine is impacted by many factors, such as age, sex, pregnancy status, obesity, smoking, and more.
Some people are more sensitive to caffeine than others, mainly because of genetic variations in enzymes responsible for breaking down caffeine in your liver.
The caffeine content found in your favorite coffee drinks varies significantly.
Larger doses of caffeine take your body longer to metabolize, which is why you’re likely to feel more energized after downing a double-shot latte compared to a cup of green tea.
Here’s the caffeine content of some of your favorite tea and coffee drinks:
- A shot (1 ounce) of espresso: around 64 milligrams (mg)
- A cup (248 grams) of black coffee: 91.8 mg
- A double-shot latte: 127 mg
- A grande Starbucks matcha latte: 65 mg
- A small Dunkin Donuts cappuccino: 118 mg
- A grande Starbucks cold brew: 205 mg
The caffeine content of drinks varies significantly depending on their specific ingredients and size. For example, a small cappuccino from Dunkin Donuts contains 118 milligrams of caffeine, while a large contains 252 milligrams.
Tip: If you’re sensitive to caffeine, pair your coffee drink with some food to slow down caffeine’s absorption into your bloodstream.
Tea generally contains less caffeine than coffee. A cup of green tea has only 28 milligrams of caffeine, while a cup of black tea contains around 47 milligrams on average.
Tea also contains compounds that may reduce anxiety, like L-theanine, an amino acid that acts on your central nervous system to reduce symptoms of stress and anxiety.
This is why sipping on a cup of matcha may provide a more calming energy than a cup of coffee.
Are you super sensitive to caffeine? Herbal teas, like peppermint tea and chamomile tea, are naturally free from caffeine and are a good option for those who want to avoid caffeinated beverages.
Having too much caffeine can lead to side effects like anxiety, rapid heartbeat, agitation, and trouble sleeping.
- It’s recommended that adults limit their caffeine intake to less than 400 milligrams per day to avoid overdosing.
- People who are sensitive to caffeine may want to limit themselves to just a cup or two of caffeinated coffee or tea per day to avoid side effects like sleeping issues and jitteriness.
- Because caffeine stays in your system for so long, it’s recommended to avoid drinking caffeinated drinks, like coffee, before bedtime.
Drinking a caffeinated drink, like a matcha latte or cold brew, can give you the energy boost you crave in the morning or midday.
But, it’s important to remember that caffeine can stay in your system for 10 hours or more.
The caffeine content of coffee and tea drinks varies considerably, so it’s important to consider caffeine content before placing your order, especially if you’re sensitive to caffeine.